LONG PUT
| Strategy Details | |
| Strategy Type | Bearish |
| # of legs | 1 |
| Maximum Reward | Unlimited |
| Maximum Risk | Limited to the extent of Put premium paid |
| Breakeven Price | Strike price -Put premium paid |
| Payoff Calculation | Maximum of (Strike Price - Underlying price, 0) - Put premium |
Explanation of the Strategy
Buying a Put is another very commonly used strategy, apart from buying a Call. Buying a Put is a bearish strategy because it gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on the expiration date. So, logically, the buyer would benefit when the underlying price would fall below the strike price, as this would enable him to exercise his/her option at a higher than the prevailing market price. For instance, if the strike price is ₹100 and the underlying price drops to ₹90, the Put holder will exercise his/her right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price of ₹100 when the asset is trading at ₹90 in the market, thereby enabling the Put buyer to profit ₹10 (which is excluding the Put premium paid to buy the option). The lower the underlying price drops below the strike price, the higher would be the buyer’s profit. On the flip side, if the underlying price rises above the strike price, the buyer will not exercise his/her Put option. In this case, the maximum loss that the buyer would incur is the Put premium that he/she has paid.
Benefits of the Strategy
-
It is a very simple strategy, as it involves only one leg
-
Limited risk, no matter how higher the underlying moves above the strike price
-
Unlimited profit potential
-
Akin to selling the underlying outright, but at a fraction of the cost
Drawbacks of the Strategy
-
Limited lifespan of Put option
-
Theta works against the Put buyer (but this could be offset by properly trading other Greeks)
-
If the underlying does not fall, there is a risk that the buyer might lose the entire premium
Moneyness of the Strategy
| If… | Option is… |
| Strike Price > Underlying Price | ITM |
| Strike Price = Underlying Price | ATM |
| Strike Price < Underlying Price | OTM |
Strategy Suggestions
-
Ensure that there is a clear downward trajectory in the price of the underlying asset or that the underlying is breaking below a consolidation zone
-
Ensure that there is sufficient time for the strategy to work out in your favour
-
If there is limited time, the buyer must have strong conviction that the underlying will fall quickly
-
Keep in mind that Theta will decay rapidly during the last few days of the life of the Put option
-
When buying a weekly Put option, avoid buying a Put that is notably OTM. Rather go with an ATM or ITM Put
-
When buying a monthly Put option, avoid buying a deep OTM Put unless you have a strong conviction that it will move ITM well inside the last few days of the option life
-
Ensure that there is sufficient liquidity in the option in which you want to create a position
Option Greeks for long Put position
| Greek | Value is | Notes |
| Delta | Negative |
Because Delta is negative, a 1pt rise in the underlying price causes the Put premium to reduce by the value of Delta, and vice versa. Delta ranges between 0 and -1 for Put options, with values closer to 0 indicating a deep OTM Put and values closer to -1 indicating a deep ITM Put. The closer the Delta to -1, the more responsive is the Put premium to changes in the underlying price, and vice versa. However, while a high Delta benefits the holder when the underlying falls, it can also cause the Put premium to decline sharply in case the underlying rises and moves towards the strike price. |
| Gamma | Positive |
Gamma is positive for long Put and causes the absolute Delta to increase as the underlying price decreases, and vice versa. Gamma is maximum when the Put is ATM and starts tapering off as the Put moves away from being ATM. When the Put is deep ITM/OTM, Gamma falls towards 0. Gamma tends to have the highest impact on Delta when the Put is ATM. Because of this, as the Put moves from ATM to ITM, the impact of Gamma on Delta tends to be higher (because absolute Delta moves above 0.5) than when the Put moves from ATM to OTM (because absolute Delta moves below 0.5). |
| Vega | Positive |
Because Vega is positive, rising IVs have a positive impact on Putpremiums, and vice versa. Vega tends to be the highest for ATM Puts and starts tapering off as the Put moves away from being ATM. Deep ITM/OTM Puts tend to have Vega close to 0. As a result, option prices tend to be the most sensitive to changes in IV when the option is ATM. Another key thing to note is that Vega will be higher for options that have a greater time to expiration, and vice versa. |
| Theta | Negative |
Because Theta is negative, it is the Put holder’s biggest enemy. This is because Put prices are negatively impacted by the passage of time. ATM Puts are subject to highest time decay because they have the highest Theta. Also, as the expiration approaches, Theta of an ATM Put rises exponentially, causing the premium to fall at a rapid pace. On the other hand, Theta does not have much impact on ITM Puts are these are mostly composed of intrinsic value. The deeper a Put gets ITM, the lesser will be the impact of Theta on premiums. Hence, buying a Put that is noticeably ITM can help to reduce the Theta exposure. |
| Rho | Negative |
Because Rho is negative, a rise in interest rates hurts the Putholder, and vice versa. However, this is the least significant of the five Greeks, because it has the least impact on the price of a Put option. |
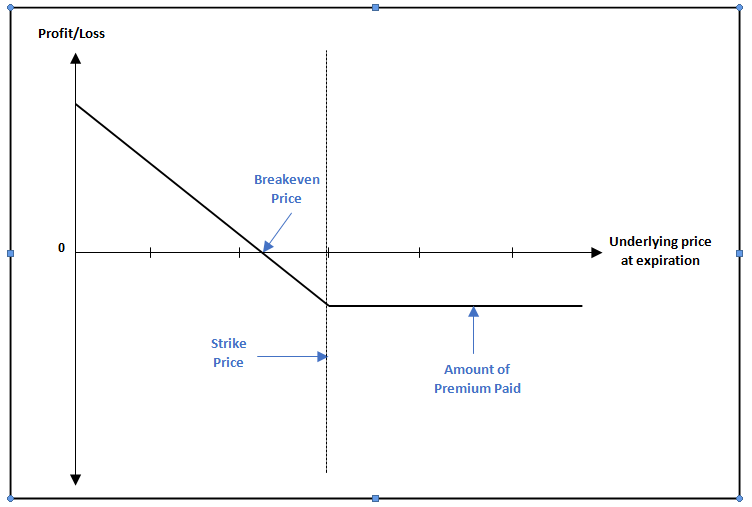
Payoff Chart for long Put position
Notice from the above chart that the Put position makes money when the underlying price drops below the breakeven price. The profit potential is unlimited (well, until the underlying price falls to 0!) once the underlying goes below the breakeven point. On the other hand, as long as the underlying price is above the strike price, the Put holder will be at a loss, which will be limited to the extent of premium paid. Between underlying price and breakeven price, the losses of the buyer will reduce, as the put premium paid will be partially recouped by the option moving ITM.
Example:
Let us assume that Bank Nifty is currently trading at 28000 and has just broken the neckline of a Double Top pattern. Based on this, I expect Bank Nifty to decline towards 27200 so long as it is below 28300. Hence, I decide to buy an ITM Put option on Bank Nifty having a strike price of 28200 at a premium of ₹300. Given that Bank Nifty has a lot size of 20, the total premium that I will have to pay to buy the Put option is ₹6,000 (₹300 * 20). Hence, I purchase the 28200 Bank Nifty PE by paying a total of ₹6,000.
-
Strike price = 28200 PE
-
Underlying price = 28000
-
Put Premium = ₹300
-
Put Premium value = ₹6,000
-
Breakeven price of this Put option = 27900 (28200-300)
Now, let us assume a few scenarios in terms of where Bank Nifty would be on the expiration date and the impact this would have on the profitability of the trade.
| Underlying price on Expiration | Net Profit/Loss | Notes |
| 30000 | Loss of ₹6,000 | Because the option is OTM, it will expire worthless. In this case, the maximum loss that the buyer will suffer is the premium value of ₹6,000 |
| 29000 | Loss of ₹6,000 | Because the option is OTM, it will expire worthless. In this case, the maximum loss that the buyer will suffer is the premium value of ₹6,000 |
| 28000 | Loss of ₹2,000 | Because the Put is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise it. However, because the buyer has paid a higher premium, he/she would still end up losing a part of the premium, amounting to ₹2,000 ((28200-28000-300)*20) |
| 27500 | Profit of ₹8,000 | Because the Put is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise it. In this case, the profit would be ₹8,000 ((28200-27500-300)*20) |
| 27000 | Profit of ₹18,000 | Because the Put is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise it. In this case, the profit would be ₹18,000 ((28200-27000-300)*20) |
| 25000 | Profit of ₹58,000 |
Because the Put is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise it. In this case, the profit would be ₹58,000 ((28200-25000-300)*20) |
As can be seen, the profits get higher and higher as the underlying price drops deeper and deeper below the breakeven price. However, the downside is fairly limited. No matter how much the underlying price rises, the maximum that the buyer of Put stands to lose is the amount of premium that has been paid. Because of limited risk and unlimited profit potential, long Put is another extremely popular strategy among traders.
Short Put
| Strategy Details | |
| Strategy Type | Bullish |
| # of legs | 1 |
| Maximum Reward | Limited to the extent of Put premium received |
| Maximum Risk | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Price | Strike price -Put premium received |
| Payoff Calculation | Put Premium - Maximum of (Strike price - Underlying price, 0) |
Explanation of the Strategy
Selling a Put option is anincome strategy, in which the sellerreceives a premium for writing the option. Because a Put option gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying, the Put seller will be obliged to buy the underlying from the Put buyer in case the latter exercises his/her right to sell the asset at the strike price. Because a long Put is a bearish strategy, it naturally follows that short Put is a bullish strategy. The seller of a Put would want the underlying price to stay above the strike price, as this would enable him/her to keep the entire premium. That said, no matter how higher the underlying price goes above the strike price, a Put seller’s profit will be limited to the extent of the option premium that he/she has received. On the flip side, a Put seller will incur losses when the underlying price drops below the breakeven price of the option, and these losses could be potentially unlimited the deeper the underlying price falls below the breakeven price. Because of this limited profit/unlimited loss scenario, Put writing might not be suitable for everyone, especially those who are new to options trading.
Benefits of the Strategy
-
It is a very simple strategy, as it involves only one leg
-
Can generate regular income, if traded well
-
The seller can benefit even if the underlying price remains sideways
-
Theta works in favour of the Put writer
Drawbacks of the Strategy
-
Potential for unlimited losses
-
Maximum reward is limited to the extent of premium received
Moneyness of the Strategy
| If… | Option is… |
| Strike Price > Underlying Price | ITM |
| Strike Price = Underlying Price | ATM |
| Strike Price < Underlying Price | OTM |
Strategy Suggestions
-
Ensure that the trend of the underlying instrument is clearly up or is range bound with a bullish bias or that there is a strong supportbelow which the underlying has been unable to sustain
-
Ensure that the life of the option is short, so that there is less potential for a sustained price decline
-
Keep in mind that Theta will work in seller’s favour during the last few days of the Put option, so this is a big advantage
-
When writing a Put option, ensure that you write an ATM Put, or better yet, a slightly OTM Put
-
Avoid writing an ITM Put option, unless you are extremely bullish on the underlying and have sufficient funds in your trading account to withstand the losses, in case the underlying declines
-
Avoid writing a Put unless you have bearish view on volatility too, as rising volatility causes the option premium to rise, all else equal
-
Ensure that there is sufficient liquidity in the option in which you want to create a short position
Option Greeks for short Put position
| Greek | Value is | Notes |
| Delta | Positive |
Because Delta is positive, a rise in the underlying price benefits the Put writer, and vice versa. A deep ITM Put has Delta closer to 1, while a deep OTM Put has Delta closer to 0. The lower the Delta, the better it is for the Put writer, and vice versa. |
| Gamma | Negative |
Because Gamma is negative, a high Gamma value can hurt a Put writer, especially if the underlying price dropsbelow the strike price as this would cause the Delta to move above 0.5 and make it more sensitive to Gamma. As Gamma tends to be at its peak for anATM Put and starts tapering off as the Put moves away from being ATM, a seller would benefit as the Put moves from ATM to OTM, because the Delta will move below 0.5 and the Gamma will start reducing, meaning its impact on Delta will start tapering off. |
| Vega | Negative |
Because Vega is negative, rising IVs hurt the Put writer, and vice versa. This is because rising IVs cause the Put premiums to rise. Instead, the seller would want the IVs to reduce, as this would lower the Put premium. |
| Theta | Positive |
Theta is the Put seller’s best friend. It is positive, meaning that the passage of time causes the Put premium to reduce, all else equal. |
| Rho | Positive |
Because Rho is positive, a rise in interest rates benefits the Put seller, and vice versa. However, this is the least significant of the five Greeks, because it has the least impact on the price of a Put option, especially ones that are shorter-dated. |
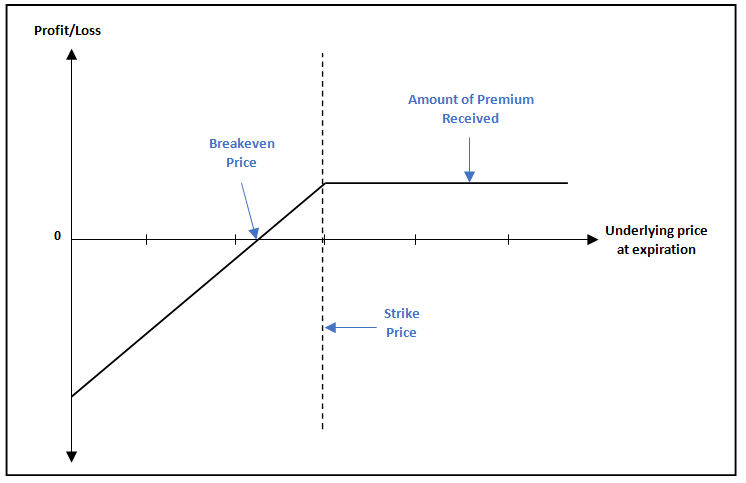
Payoff Chart for short Put position
We can observe from the above chart that as long as the underlying price is above the strike price, the Put seller gets to keep the entire premium amount that he/she has received upfront. As we can see, this is the maximum profit a Put seller can earn, no matter how higher the underlying price goes above the strike price. When the underlying price falls below the strike price but is above the breakeven price, the Put seller’s profit potential starts reducing, which can be calculated as the amount of premium received less the difference between the strike price and the underlying price. Meanwhile, when the underlying price falls below the breakeven price, the Put seller will start suffering losses, which can be potentially unlimited (well, at least until the underlying price drops to zero). Because of this limited reward and unlimited risk payoff, Putwriting strategy might not be suitable to everyone, especially when it is done naked.
Example :
Let us assume that Bank Nifty is currently trading at 27800 and that for the past few days it has been unable to break below 27600, which is acting as a strong support. Given this, I expect Bank Nifty to attempt a modest rebound as long as it is above 27600. Hence, I decide to write an OTM Put option on Bank Nifty having a strike price of 27600 for a premium of ₹200. Given that Bank Nifty has a lot size of 20, the total premium that I will receive to sell the Put option is ₹4,000 (₹200 * 20). Hence, I write the 27600 Bank Nifty PE and receive a total of ₹4,000.
-
Strike price = 27600 PE
-
Underlying price = 27800
-
Put Premium = ₹200
-
Put Premium value = ₹4,000
-
Breakeven price of this Put option = 27400 (27600-200)
Now, let us assume a few scenarios in terms of where Bank Nifty would be on the expiration date and the impact this would have on the profitability of the trade.
| Underlying price on Expiration | Net Profit/Loss | Notes |
| 26000 | Loss of ₹28,000 | As this option is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise his right to sell the underlying at 27600. In this case, the seller will suffer a loss of ₹28,000 ((200-27600+26000)*20) |
| 26500 | Loss of ₹18,000 | As this option is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise his right to sell the underlying at 27600. In this case, the seller will suffer a loss of ₹18,000 ((200-27600+26500)*20) |
| 27000 | Loss of ₹8,000 | As this option is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise his right to sell the underlying at 27600. In this case, the seller will suffer a loss of ₹8,000 ((200-27600+27000)*20) |
| 27500 | Profit of ₹2,000 | As this option is expiring ITM, the buyer will exercise his right to sell the underlying at 27500. However, as the premium received exceeds the difference between the underlying price and the strike price, the seller will still make a gain to the tune of ₹2,000 ((200-27600+27500)*20) |
| 28000 | Profit of ₹4,000 | Because the option is expiring OTM, the buyer will not exercise the option. Hence, the seller will get to keep the entire premium amount of ₹4,000 |
| 28500 | Profit of ₹4,000 | Because the option is expiring OTM, the buyer will not exercise the option. Hence, the seller will get to keep the entire premium amount of ₹4,000 |
| 29000 | Profit of ₹4,000 | Because the option is expiring OTM, the buyer will not exercise the option. Hence, the seller will get to keep the entire premium amount of ₹4,000 |
As we can see from the above table, if the view of the Put seller goes wrong and if he/she holds on to the position till expiration, the losses could get pretty huge. Hence, it becomes very prudent for the writer to monitor his/her short Put position very closely, especially once the underlying price drops below the breakeven price. On the other hand, observe that the profit that the writer can earn is limited to the extent of premium that he/she has received from the seller. No matter how higher the underlying price goes above the breakeven price, the seller’s profit will be capped at the amount of premium.
Next Chapter
Comments & Discussions in
FYERS Community