

 27 Jul, 2025
27 Jul, 2025
 3 mins read
3 mins read
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses the Cash Reserve Ratio as a key monetary policy tool to regulate liquidity, control inflation, and ensure financial stability in the banking system. By requiring banks to maintain a fixed portion of their deposits with the RBI, CRR directly influences how much money banks can lend thereby shaping the flow of credit in the economy.
The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the minimum percentage of a commercial bank’s total deposits that it must keep in the form of cash reserves with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This means banks are required to hold a certain portion of their deposit liabilities as cash, which they cannot use for lending or investment purposes.
The CRR is a tool used by the RBI to control liquidity in the banking system. By increasing the CRR, the RBI can reduce the amount of money available for banks to lend, thereby tightening the money supply. Conversely, reducing the CRR increases liquidity in the system.
Here is how CRR works in practice:
RBI sets the CRR rate
Banks calculate their NDTL
They must hold that percentage in cash with RBI
RBI reviews compliance fortnightly
Managing CRR helps RBI regulate the money supply. Raising CRR tightens liquidity and curbs inflation. Lowering it frees up funds for lending and economic growth.
Here are the key objectives of CRR:
Liquidity control: Ensures banks hold enough liquid cash
Inflation management: Reduces excess money in the system
Safety net: Helps banks handle large withdrawals
Monetary discipline: Prevents over-lending by banks
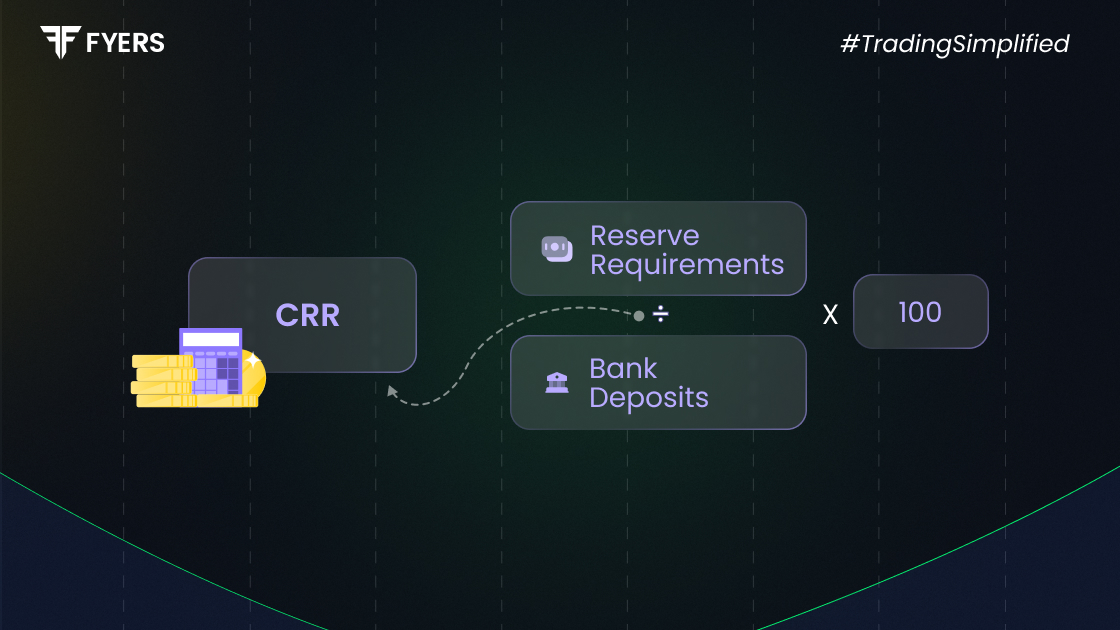
Use this cash reserve ratio formula:
|
CRR = (Cash Reserve / NDTL) × 100 |
CRR calculation example:
If a bank’s NDTL is ₹50,000 crore and CRR is set at 4%, it must hold ₹2,000 crore with the RBI.
While both are regulatory tools, CRR and SLR differences paint a different picture.
|
Feature |
CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) |
SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) |
|---|---|---|
|
Full Form |
Cash Reserve Ratio |
Statutory Liquidity Ratio |
|
Requirement |
Kept with RBI in cash |
Held in gold, cash or approved securities |
|
Objective |
Regulate money supply |
Ensure bank solvency |
|
Interest |
No interest paid by RBI |
Banks earn interest |
|
Impact on Lending Capacity |
Directly reduces cash for loans |
Reduces lending depending on holdings |
The cash reserve ratio is a vital tool in India’s monetary policy. It ensures banks maintain stability and manage liquidity. It also helps the RBI control inflation and influence economic activity. For banks, it limits lending capacity but improves risk management. For observers, any change in CRR provides a clue about the central bank’s policy direction.
CRR full form is Cash Reserve Ratio. It is the portion of deposits that banks must hold with the RBI in cash.
Banks maintain CRR to comply with RBI regulations and to ensure liquidity in the system.
Higher CRR reduces liquidity and controls inflation. Lower CRR boosts liquidity, which may increase inflation.
The current CRR rate is 3% as of March 2025.
CRR influences how much banks can lend. Higher CRR means less lending and slower economic activity. Lower CRR means more lending and growth.
Calculate your Net P&L after deducting all the charges like Tax, Brokerage, etc.
Find your required margin.
Calculate the average price you paid for a stock and determine your total cost.
Estimate your investment growth. Calculate potential returns on one-time investments.
Forecast your investment returns. Understand potential growth with regular contributions.