

 20 Mar, 2025
20 Mar, 2025
 5 mins read
5 mins read
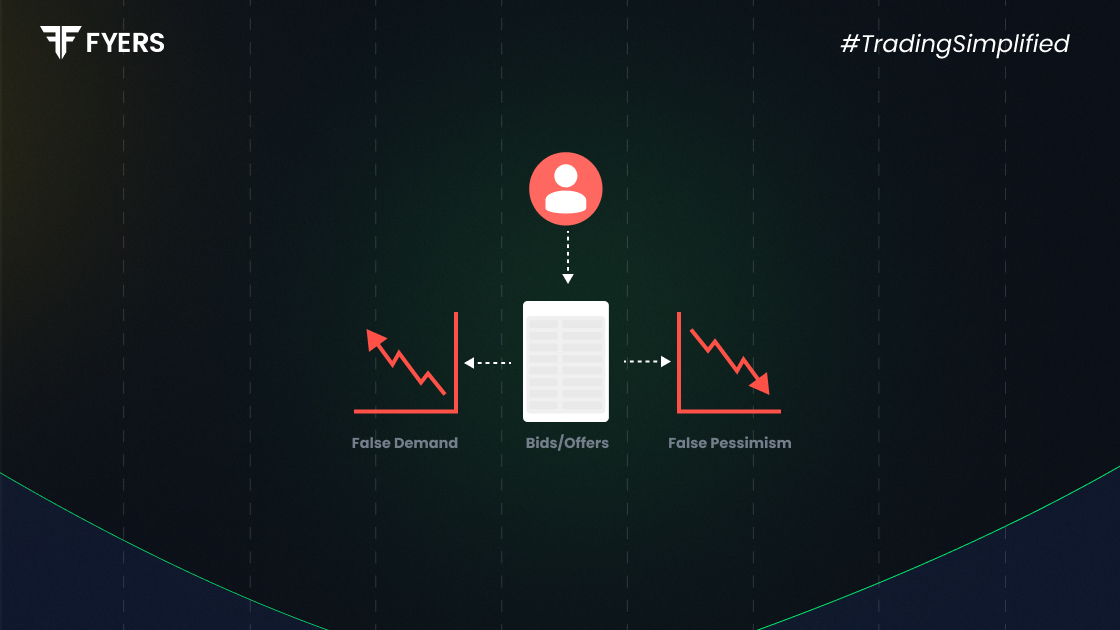
Spoofing in trading is a deceptive practice where traders place fake buy or sell orders to manipulate market prices. It misleads investors, distorts supply and demand, and creates artificial price movements. Due to its fraudulent nature, spoofing is illegal in India and closely monitored by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Let’s explore what spoofing is, how it works, and how traders can detect and prevent it in the Indian stock market.
Spoofing in trading refers to the practice of placing large buy or sell orders without intending to execute them. These fake orders create a misleading impression of demand or supply, tricking other traders into reacting. Once the market moves in the desired direction, the spoofer cancels the orders and profits from the artificial price movement.
Spoofing is commonly seen in high-frequency trading (HFT) and automated trading systems, where rapid order placement and cancellations can easily mislead investors.
Spoofing exploits market psychology and automated trading algorithms. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
Placing Fake Orders: A trader places large buy or sell orders to create a false sense of demand or supply.
Influencing Market Sentiment: Other traders react, assuming a price increase or decrease is imminent.
Executing Real Trades: The spoofer executes smaller trades in the desired direction before canceling the fake orders.
Cancelling the Spoof Orders: The trader removes the fake orders, causing the market to revert and locking in profits.
This strategy manipulates prices momentarily, creating opportunities for quick profits at the expense of unsuspecting traders.
To understand spoofing better, let’s look at a few spoofing trading examples:
Stock Market Spoofing: A trader places a large buy order for a popular stock listed on the NSE at ₹500.10, attracting buyers. Meanwhile, they sell their existing shares at ₹500.09. Once their sales are complete, they cancel the buy order, causing the stock price to drop.
Futures Market Spoofing: A trader in Nifty or Bank Nifty futures places massive sell orders, pushing prices lower. They then buy at a lower price and cancel the initial sell orders.
Cryptocurrency Spoofing: In Bitcoin trading on Indian crypto exchanges, a manipulator places huge buy orders at ₹32,00,000, leading others to buy in fear of missing out. The spoofer then sells at a higher price and removes the buy orders.
These tactics artificially impact price action, misleading traders into making poor decisions.
Yes, spoofing is illegal in India. SEBI, the country’s market regulator, has strict guidelines against market manipulation practices like spoofing. The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956, and SEBI’s Prohibition of Fraudulent and Unfair Trade Practices (PFUTP) regulations outline heavy penalties for such activities.
Traders found guilty of spoofing can face:
Heavy fines
Trading bans
From April 5, 2024 onwards, SEBI has laid strict regulations to stop spoofing. Traders who try to modify their orders repeatedly without really placing the orders will face temporary trading ban. Their accounts will be disabled for anytime between 15 minutes to 2 hours upon detection of the violation. SEBI uses advanced surveillance tools to detect and penalise spoofers, ensuring a fair trading environment for retail and institutional investors.
The duration of the ban will depend on the extent of the violation.
In April 2023, SEBI took action against Nimi Enterprises for manipulating the stock market through spoofing, a deceptive trading practice. The company placed large orders at unrealistic prices to create a false impression of demand or supply, while executing smaller trades at market rates. Shortly after, the large orders were canceled, misleading other investors.
Stock market rules require traders to disclose either their full order or at least 10% of it, but Nimi Enterprises only revealed its smaller trades, hiding the bigger ones. SEBI found this to be a clear violation of regulations.
As a result, SEBI banned the company from the securities market for two years and fined it ₹2 lakh. This action reinforces SEBI’s commitment to keeping the market fair and protecting investors.
Detecting spoofing requires a keen eye on order book activity and unusual patterns. Here are some key indicators:
Large Orders Without Execution: If a trader repeatedly places and cancels large orders, it may be spoofing.
Discrepancies in Buy/Sell Orders: A large imbalance between buy and sell orders can indicate manipulation.
Rapid Order Cancellations: Orders placed and canceled within seconds, with no real execution, are a red flag.
Price Reversals After Order Cancellations: If prices move sharply after large orders vanish, it suggests artificial influence.
Traders can use specialised trading tools and analytics software to monitor these patterns and avoid falling into spoofing traps.
While spoofing is illegal, some legitimate trading strategies may appear similar at first glance. Here’s how they differ:
|
Aspect |
Spoofing |
Legitimate Trading |
|---|---|---|
|
Intent |
To manipulate prices |
To execute real trades |
|
Order Execution |
Orders are canceled before execution |
Orders are filled as planned |
|
Market Impact |
Creates false demand/supply |
Reflects genuine market activity |
|
Legality |
Illegal |
Legal |
Spoofing in trading is a serious offense that can distort market integrity and harm investors. Understanding how spoofing works, how to identify it, and its legal consequences can help traders navigate the Indian stock market safely. By staying informed and vigilant, investors can protect themselves from market manipulation and make informed trading decisions.
No, spoofing is illegal in India. SEBI strictly prohibits such market manipulation practices, and traders caught engaging in spoofing can face severe penalties.
Traders can detect spoofing by analysing order book activity, watching for large orders that disappear quickly, and tracking price movements before and after major order cancellations.
Penalties for spoofing in India include hefty fines, and trading restrictions, charges.
Market-making involves placing buy and sell orders to provide liquidity, while spoofing involves deceptive orders meant to manipulate prices. Market-making is legal, whereas spoofing is fraudulent.
To detect spoofing in trading, watch for large orders that get canceled frequently without execution. Use trading analytics tools to track rapid order placements and withdrawals. Price movements reversing immediately after order cancellations can also be a strong indicator of spoofing.
Calculate your Net P&L after deducting all the charges like Tax, Brokerage, etc.
Find your required margin.
Calculate the average price you paid for a stock and determine your total cost.
Estimate your investment growth. Calculate potential returns on one-time investments.
Forecast your investment returns. Understand potential growth with regular contributions.