

 19 Mar, 2025
19 Mar, 2025
 4 mins read
4 mins read
The reverse repo rate is one of the key tools used by central banks to regulate liquidity in the financial system. It plays a crucial role in shaping monetary policy, controlling inflation, and maintaining economic stability. Whether you are an investor, a borrower, or simply someone interested in financial markets, understanding the reverse repo rate can help you grasp how interest rates and liquidity work in an economy. This article breaks down the concept, its working mechanism, its significance, and how it differs from the repo rate.
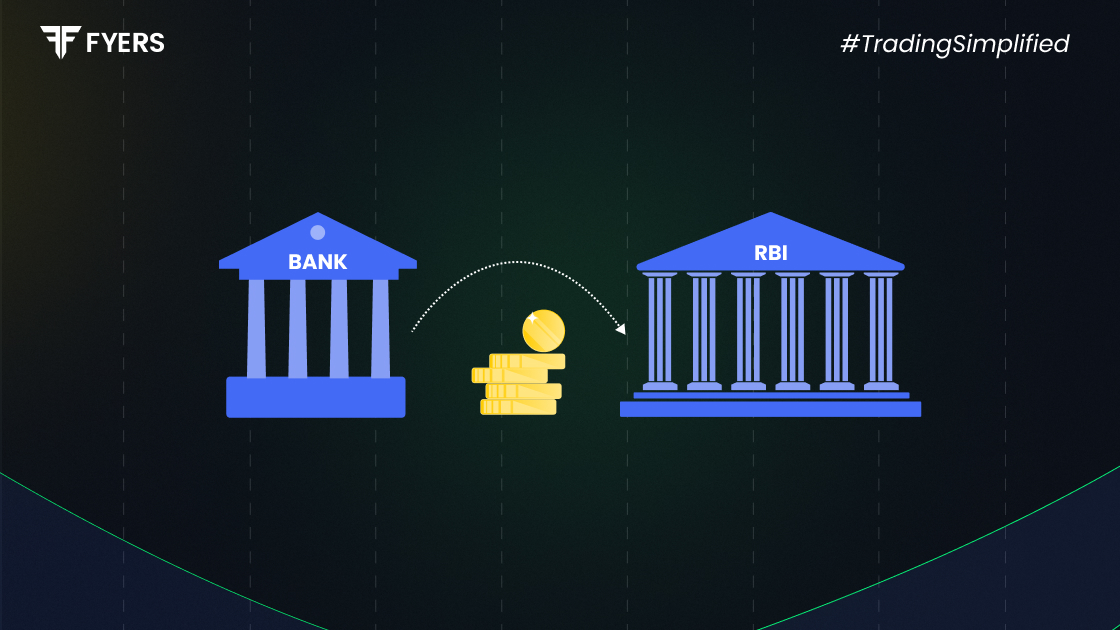
The reverse repo rate is the interest rate at which the central bank of a country borrows money from commercial banks. In India, this rate is set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It acts as a tool for controlling liquidity in the banking system.
To put it simply, when banks have surplus cash, they can park it with the RBI and earn interest at the reverse repo rate. This mechanism helps in absorbing excess funds from the economy, thereby controlling inflation.
To understand how reverse repo rate works, let’s consider a scenario:
When there is excess liquidity in the economy, banks have extra cash that they need to invest.
Instead of lending it to businesses or individuals, they deposit it with the RBI and earn interest at the reverse repo rate.
The RBI, in return, reduces the available cash in the market, thereby controlling inflation and stabilising the economy.
For instance, if inflation is rising, the RBI may increase the reverse repo rate. This encourages banks to deposit their funds with the RBI instead of lending, reducing the money supply in the economy.
The reverse repo rate plays a crucial role in the monetary policy framework. It helps in:
Liquidity Management - By adjusting the reverse repo rate, the central bank can control the amount of money circulating in the economy.
Inflation Control - When inflation is high, increasing the reverse repo rate reduces excess liquidity, helping to curb price rises.
Financial Stability - A balanced reverse repo rate ensures that banks have a safe avenue for surplus funds, reducing risky lending practices.
Interest Rate Management - The reverse repo rate indirectly influences other interest rates in the economy, including deposit and loan rates.
Changes in the reverse repo rate can have significant effects on various aspects of the economy:
On Inflation: A higher reverse repo rate absorbs excess liquidity, controlling inflation. Conversely, a lower reverse repo rate increases liquidity, potentially boosting inflation.
On Borrowing and Lending: When the reverse repo rate rises, banks prefer to deposit their money with the RBI instead of lending, making loans more expensive. A lower reverse repo rate encourages banks to lend more, making credit cheaper.
On Economic Growth: A lower reverse repo rate stimulates growth by encouraging borrowing and investment. A higher reverse repo rate can slow down growth to prevent overheating of the economy.
Many people wonder about the difference between reverse repo rate and repo rate. While both are crucial monetary policy tools, they serve different purposes.
|
Aspect |
Repo Rate |
Reverse Repo Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
Meaning |
The rate at which banks borrow from the RBI. |
The rate at which banks deposit surplus funds with the RBI. |
|
Purpose |
Injects liquidity into the economy. |
Absorbs excess liquidity from the economy. |
|
Impact on Loans |
Higher repo rate makes loans costlier. |
A higher reverse repo rate reduces liquidity, indirectly affecting loans. |
|
Effect on Economy |
A lower repo rate is used to encourage borrowing and spending. |
Used to control inflation and excess money supply. |
Thus, what is the repo and reverse repo rate difference? The difference lies in their function - one infuses money into the economy, while the other withdraws it.
Over the years, the RBI has adjusted the reverse repo rate based on economic conditions. For example:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the RBI reduced the reverse repo rate to encourage banks to lend more.
In times of high inflation, the RBI increases the reverse repo rate to absorb excess liquidity and control price rises.
As of February 7, 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained the reverse repo rate at 3.35%. This decision reflects the RBI's ongoing efforts to balance economic growth with inflation control. The reverse repo rate remains a pivotal instrument in the central bank's monetary policy toolkit, influencing liquidity, interest rates, and overall economic stability. Understanding its mechanisms and implications is essential for comprehending the broader economic landscape and making informed financial decisions.
In simple terms, the reverse repo rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks deposit their surplus funds with the central bank. It helps control liquidity and inflation in the economy.
When the reverse repo rate increases:
Changes in the reverse repo rate indirectly impact loan interest rates:
Calculate your Net P&L after deducting all the charges like Tax, Brokerage, etc.
Find your required margin.
Calculate the average price you paid for a stock and determine your total cost.
Estimate your investment growth. Calculate potential returns on one-time investments.
Forecast your investment returns. Understand potential growth with regular contributions.