

 28 Feb, 2025
28 Feb, 2025
 4 mins read
4 mins read
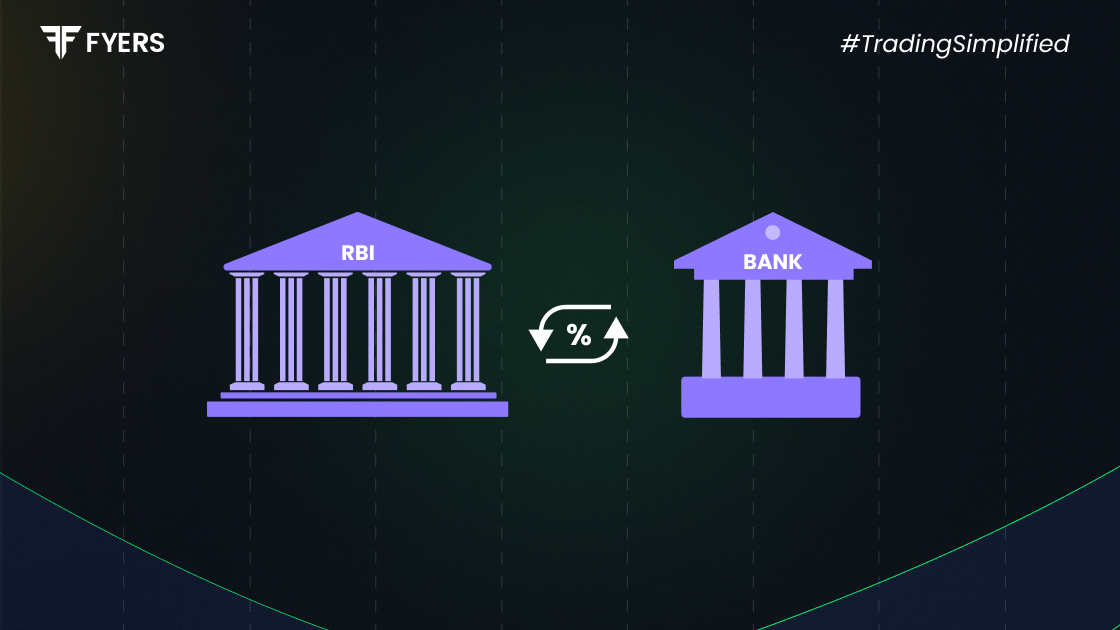
In today’s financial world, the repo rate plays a crucial role in shaping a country’s economy. It influences everything from loan interest rates to inflation. But what exactly is the repo rate, and how does it affect you? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
The repo rate definition is quite simple: It is the interest rate at which the central bank of a country (like the Reserve Bank of India) lends money to commercial banks in exchange for government securities.
In other words, if a bank needs short-term funds, it can borrow money from the RBI at the repo rate. This helps banks manage their short-term liquidity needs and ensure the smooth functioning of the financial system.
For example, if the RBI sets the repo rate at 6%, banks borrowing money from the RBI will have to pay an interest of 6% on the borrowed amount.
Imagine a commercial bank running low on cash reserves - instead of facing a liquidity crisis, the bank approaches the RBI, offers government securities as collateral, and borrows money at the repo rate.
Here’s a step-by-step process of how it works:
A commercial bank pledges government securities as collateral to the RBI.
The RBI lends money to the bank at the prevailing repo rate.
Once the bank has sufficient liquidity, it repays the borrowed amount along with interest.
The RBI returns the pledged securities after the loan is settled.
This mechanism ensures that banks always have access to emergency funds, preventing financial instability.
Many people wonder why the repo rate is important. The repo rate directly affects various aspects of the economy, including:
Inflation Control:
When inflation rises, the RBI increases the repo rate, making borrowing expensive for banks. As a result, banks lend less, reducing the money supply and slowing inflation.
Conversely, when inflation is low, the RBI reduces the repo rate, encouraging borrowing and increasing cash flow in the economy.
Loan and EMI Rates:
The repo rate influences the interest rates on loans. If the repo rate goes up, banks pass the cost to customers by increasing loan interest rates, making home loans, car loans, and business loans costlier.
On the other hand, a lower repo rate leads to cheaper loans, boosting spending and economic growth.
Economic Growth:
A lower repo rate promotes business expansion and consumer spending, leading to higher GDP growth.
A higher repo rate slows down economic activity to control inflation.
People often wonder what is the current repo rate to stay updated on lending rates. As of February 2025, the current repo rate in India is 6.25%. The RBI reviews the rate periodically and adjusts it based on inflation, economic growth, and other factors.
To stay updated, check the RBI’s official website or financial news portals for the latest changes.
The repo rate calculation is determined by the RBI based on multiple economic indicators such as:
Inflation Rates: High inflation leads to an increase in the repo rate to control excessive money supply.
Economic Growth: If the economy is sluggish, the RBI may lower the repo rate to encourage spending and investments.
Liquidity Conditions: If banks have excess liquidity, the RBI may not need to adjust the repo rate frequently.
Government Monetary Policies: The RBI aligns the repo rate with the government’s broader financial goals.
The RBI does not use a fixed mathematical formula to determine the repo rate but instead bases its decision on these factors.
The repo rate has fluctuated over the years based on economic conditions. Here’s a quick look at its history:
2020: Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the RBI reduced the repo rate to 4% to boost economic recovery.
2022: With rising inflation, the RBI gradually increased the repo rate to 6.50%.
2023-2024: The repo rate has remained stable at 6.50% due to high inflation.
2025: The repo rate was reduced to 6.25% to boost consumption.
Monitoring these changes helps businesses and individuals make informed financial decisions.
Understanding the repo rate is essential for anyone looking to stay informed about financial and economic trends. From influencing loan EMIs to controlling inflation, the repo rate plays a key role in shaping a country’s economic landscape. Keeping track of the current repo rate in India and its fluctuations can help individuals and businesses make smarter financial decisions.
The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks when they are short on funds. A higher repo rate makes loans expensive, while a lower repo rate makes borrowing cheaper.
A high repo rate is good for controlling inflation but bad for borrowers as it increases loan interest rates. A low repo rate boosts borrowing and spending but may lead to inflation.
The repo rate is lower than the bank rate because it involves secured lending.
When the RBI increases the reverse repo rate, banks prefer to park their money with the RBI instead of lending, reducing liquidity in the economy.
Calculate your Net P&L after deducting all the charges like Tax, Brokerage, etc.
Find your required margin.
Calculate the average price you paid for a stock and determine your total cost.
Estimate your investment growth. Calculate potential returns on one-time investments.
Forecast your investment returns. Understand potential growth with regular contributions.