

 23 Jul, 2025
23 Jul, 2025
 4 mins read
4 mins read
The CASA ratio has long been a key metric for assessing the financial health and cost-efficiency of Indian banks. But as digital banking continues to evolve, so too does the structure of deposits in current and savings accounts. In this blog, we’ll explore what CASA ratio means, how digitalization is changing customer behavior, and the implications for Indian banks.
CASA ratio stands for Current Account and Savings Account ratio. It represents the proportion of a bank’s total deposits held in these low-cost accounts. A higher CASA ratio indicates that a larger portion of a bank’s funds comes from accounts that do not earn high interest, helping reduce overall funding costs.
A healthy CASA ratio allows banks to:
Lower their cost of capital
Increase lending margins
Improve profitability
Maintain liquidity during uncertain times
In today’s digital economy, where deposit mobilization is increasingly technology-driven, the CASA ratio has become even more dynamic.
CASA accounts comprise two types:
Current Account: Mainly used by businesses, these accounts allow unlimited transactions but do not earn interest.
Savings Account: Designed for individuals, these accounts earn modest interest but have transaction limits.
Both types of deposits are cost-effective for banks compared to fixed deposits or bulk term deposits. Thus, banks aim to attract as much CASA as possible to fund loans at better margins.
Current account benefits for businesses include:
High transaction limits or no cap
Easy fund transfers
Overdraft facilities
Seamless integration with payment gateways and ERP systems
From a banking perspective, current accounts are interest-free, making them the cheapest source of funds. In the CASA mix, a strong base of current account holders—especially SMEs and large corporates—can significantly lift the ratio.
The rise of digital banking—through mobile apps, UPI, internet banking, and fintech partnerships—has redefined how deposits are acquired and retained.
Key trends influencing CASA:
UPI and QR-based transactions have replaced physical banking, encouraging more people to open savings accounts digitally.
Video KYC and paperless onboarding reduce the friction of opening accounts.
Neo-banking platforms and digital NBFCs provide seamless current account experiences tailored for start-ups and SMEs.
Custom mobile dashboards and app notifications increase user engagement and encourage savings.
This digital transformation is making CASA acquisition faster, cheaper, and more accessible.
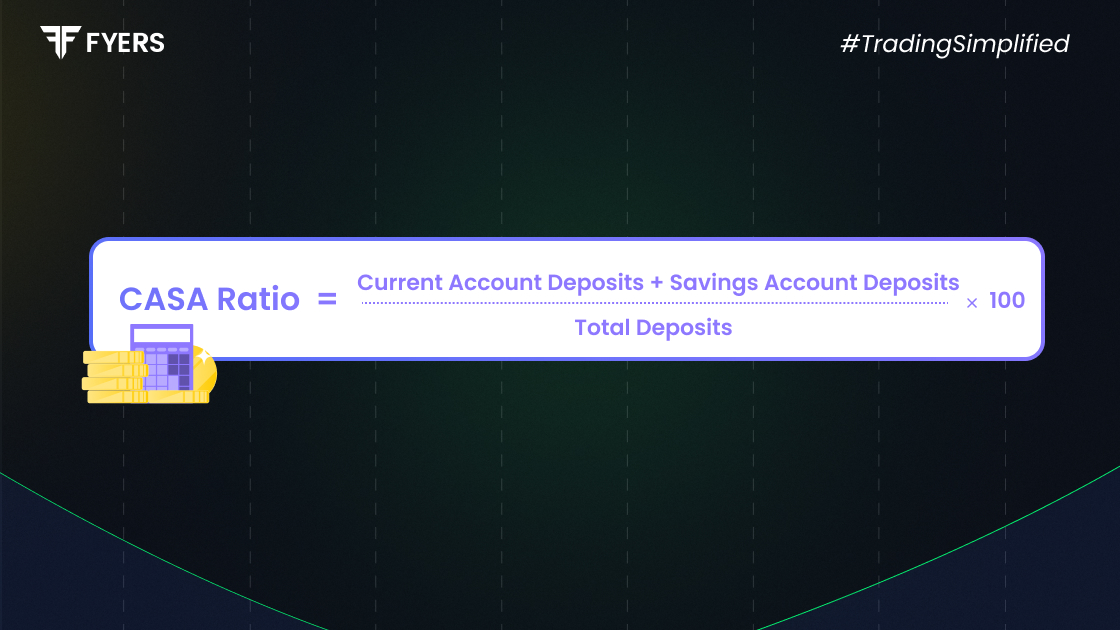
The CASA ratio formula is:
CASA Ratio = (Current Account Deposits + Savings Account Deposits) ÷ Total Deposits × 100
For example, if a bank has ₹1,00,000 crore in total deposits, and ₹40,000 crore in CASA deposits, the CASA ratio is:
(40,000 / 1,00,000) × 100 = 40%
Banks track this ratio monthly or quarterly, often comparing performance across branches and digital vs. physical acquisition channels.
Digitalization has created new deposit avenues:
Salary accounts linked to corporate tie-ups through fintech APIs
Mobile-first savings products with cashback or rewards to attract Gen Z
Business banking apps for seamless current account management
With growing smartphone penetration in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, rural CASA mobilization is also on the rise. Even small traders now open digital current accounts to accept UPI payments, directly lifting the CASA base.
Despite digital growth, Indian banks face several hurdles:
Increased competition from FinTech's and payment banks
Customer churn due to poor digital user experience
Lower interest rates on savings, prompting users to shift funds to mutual funds or digital FDs
High-value customers expecting premium digital services and personalization
In addition, public sector banks still lag behind private peers in digital adoption, though some are catching up via app revamps and fintech partnerships.
Banks are taking several digital-first steps to improve their CASA metrics:
Gamified savings apps to attract younger savers
AI-driven financial planning tools embedded in mobile banking
Bundled offerings (e.g. zero balance savings accounts with digital wallets or insurance)
Business onboarding APIs for instant current account activation
Customized alerts to prevent dormant account closures
By aligning digital innovation with customer convenience, banks can sustainably grow their CASA base without relying on branch expansion.
The CASA ratio remains a crucial metric for assessing banking strength, especially in a competitive credit environment. As digital banking reshapes how individuals and businesses interact with financial institutions, CASA strategies are also undergoing transformation. Indian banks that prioritize frictionless digital onboarding, seamless experiences, and value-added services are likely to maintain healthier CASA ratios in the years ahead.
CASA ratio measures the proportion of total deposits in current and savings accounts. A higher CASA ratio indicates lower-cost funding for banks.
CASA accounts provide low-cost deposits that boost bank profitability, improve lending margins, and support liquidity.
CASA Ratio = (Current Account + Savings Account Deposits) ÷ Total Deposits × 100
Current accounts offer unlimited transactions, easy payments, and integration with business tools—ideal for SMEs and corporates.
Calculate your Net P&L after deducting all the charges like Tax, Brokerage, etc.
Find your required margin.
Calculate the average price you paid for a stock and determine your total cost.
Estimate your investment growth. Calculate potential returns on one-time investments.
Forecast your investment returns. Understand potential growth with regular contributions.